Hvordan oppnår det sentrale venekatetersettet medisinske formål gjennom synergi av forskjellige komponenter?
Analyse av kjernekomponentene i settet
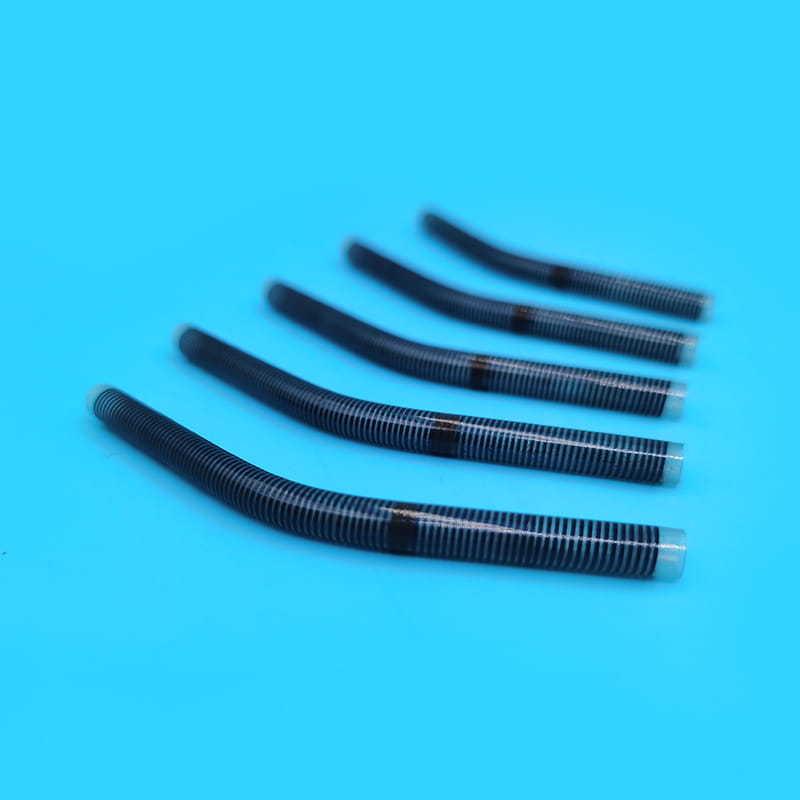
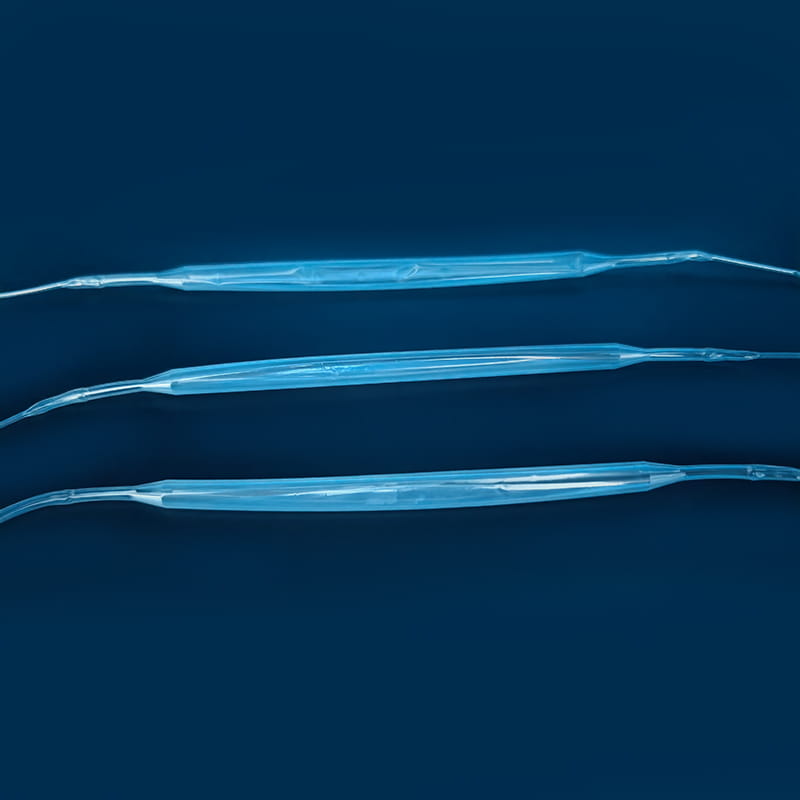
De Central Venous Catheter Kit Inneholder en rekke viktige komponenter, som hver spiller en unik og uerstattelig rolle i hele den medisinske operasjonsprosessen. Den første er det sentrale venekateteret, som er kjernekomponenten i settet og er kanalen som forbinder den sentrale vene utenfor kroppen og inne i kroppen. Materialet er vanligvis laget av medisinsk kvalitet polyuretan eller silikon. Slike materialer har god biokompatibilitet og kan effektivt redusere kroppens avvisning av fremmedlegemer og redusere risikoen for komplikasjoner som infeksjon. Ulike typer sentrale venekateter har sine egne egenskaper i struktur og funksjon. Enkeltlysekateter er egnet for enkeltbehandlingsbehov, mens dobbeltlumen eller flerlysekateter kan utføre en rekke forskjellige medisinske operasjoner samtidig, for eksempel infusjon, blodinnsamling og medikamentadministrasjon, noe som forbedrer effektiviteten og bekvemmeligheten av medisinsk drift. Når det gjelder design, behandles noen kateteroverflater med spesielle belegg for å forbedre anti-trombotiske egenskaper ytterligere; Noen er også merket med skalaer for å lette medisinsk personell for å forstå innsettingsdybden nøyaktig.
De cannula plays a pioneering role in the central venous catheter kit. When performing a central venous catheter insertion operation, the cannula is first used for percutaneous puncture into the vein. Its needle tip adopts a bevel cutting process. This design is sharp and precise, and can quickly and accurately penetrate the skin and vein wall with minimal resistance, opening a channel for the entry of subsequent components. The needle core and outer sleeve of the cannula needle are closely matched. When the cannula needle successfully enters the vein, the inner needle core is removed through a special separation mechanism, and the outer sleeve with a certain hardness and flexibility will remain in the vein as a guide channel for subsequent guide wires and other components to enter. To ensure the accuracy of puncture, some cannula needles are also equipped with ultrasound guidance adapters, which can be used with ultrasound equipment to observe the puncture path and blood vessel status in real time.
De guidewire is a key tool for precise positioning and guidance in the central venous catheter kit. After the cannula needle establishes the initial channel, the guidewire will be sent into the vein through the cannula. The outer layer of the guidewire is usually woven from medical-grade stainless steel wire, and the inner layer is a nickel-titanium alloy core. This structure gives the guidewire good flexibility and maneuverability. Doctors can use the J-shaped or straight head design of the guidewire tip to flexibly turn and guide it in the blood vessel through in vitro operation, and accurately send it to the target position. Some high-end guidewires also have a hydrophilic coating, which becomes lubricated after contact with blood, further reducing friction damage to the inner wall of the blood vessel. The existence of the guidewire makes the insertion path of the central venous catheter clearer and more controllable, laying a solid foundation for the smooth insertion of the subsequent catheter.
De role of the dilator in the central venous catheter kit should not be ignored. Since the diameter of the vein is relatively thin, and the central venous catheter needs to be smoothly inserted, it is necessary to properly dilate the vein. The dilator usually adopts a conical or cylindrical design, and the material is mostly medical-grade polyethylene. It can enter the vein along the guidewire and expand the channel of the venous puncture site by gradually expanding. During the expansion process, the smooth surface treatment and gradual caliber design of the dilator can reduce damage to the venous tissue while ensuring effective expansion. For special patients, such as those with thin blood vessel walls or sclerosis, there are also special controllable dilators available, and doctors can accurately adjust the expansion strength and range according to actual conditions.
De peelable sheath is an important part of the central venous catheter kit to ensure the safe insertion of the catheter. After the dilator completes the dilation of the vein, the peelable sheath will be sent into the vein along the guidewire and dilator. The peelable sheath consists of two symmetrical half sheaths connected by a special locking structure in the middle. When the peelable sheath reaches the appropriate position, the central venous catheter will be inserted into the vein through the sheath. At this time, the medical staff will separate the peelable sheath from the middle lock and remove it from the body through a specific operation technique, while the central venous catheter will be left in the vein. This unique design not only ensures the smooth catheter insertion process, but also avoids unnecessary damage to the vein and catheter. To prevent accidental scratches on the surrounding tissue when the sheath is peeled off, the edge of the sheath is specially rounded and blunted.
De fixing device plays a role in stabilizing and fixing the catheter in the central venous catheter kit. In order to ensure that the central venous catheter can maintain a stable position in the patient's body for a long time without displacement or falling off, fixing devices such as sutures, sterile dressings or special catheter fixers will be used to fix the catheter to the patient's skin. The suture fixation method is suitable for patients with long-term catheterization. The catheter is fixed to the skin tissue through delicate suturing operations; the sterile dressing is breathable, waterproof and antibacterial, and can effectively protect the puncture site; the dedicated catheter fixator is made of medical-grade silicone or polymer materials, and can be personalized according to the patient's skin morphology and catheter model through an adjustable buckle design. Appropriate fixation can not only ensure the normal function of the catheter, but also reduce the discomfort and potential risks caused to the patient by the movement of the catheter.
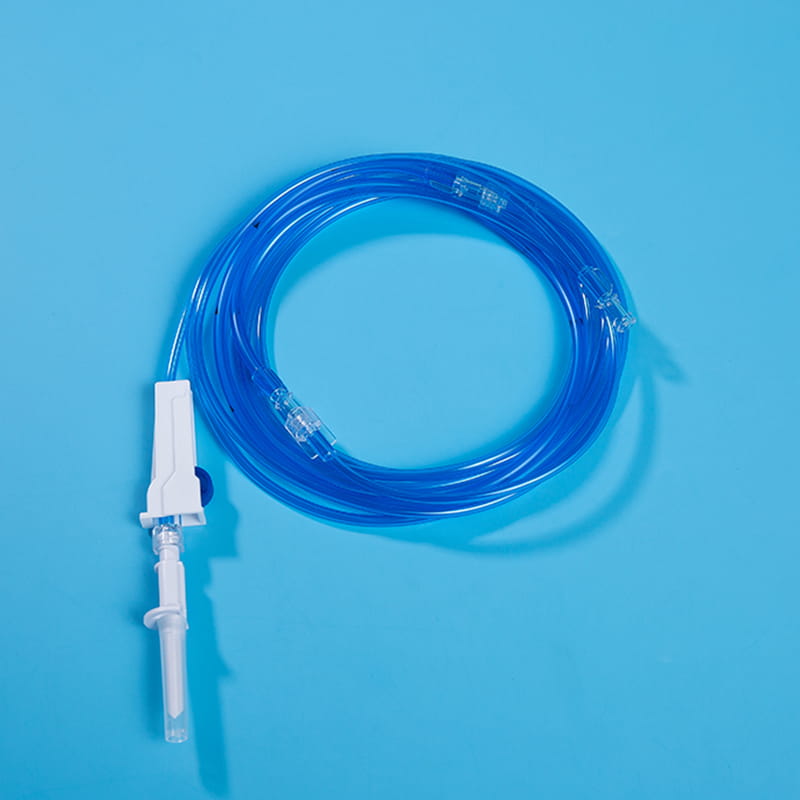
De interface for external connection is the bridge between the central venous catheter and external medical equipment. Through these interfaces, the central venous catheter can be connected to infusion sets, syringes and other equipment to achieve various medical operations such as infusion, drug administration, and blood collection. The design of these interfaces has good sealing and compatibility, and common ones include Luer connectors and needleless infusion connectors. The Luer connector is connected by threads to ensure a tight connection without leakage; the needleless infusion connector adopts a diaphragm design, which can complete the infusion operation without acupuncture, reducing the risk of infection. At the same time, some interfaces also have anti-backflow function to prevent blood from reflux and blocking the catheter, and support multiple devices to be connected at the same time to meet complex clinical needs.
Bredt spekter av kliniske applikasjonsscenarier
I faktiske medisinske anvendelser er bruksscenariene for sentrale venekatetersett veldig brede. Innen intensivavdeling, for pasienter med kritiske tilstander som trenger en stor mengde infusjon og hyppige medisiner, kan sentrale venekateter gi en rask og stabil infusjonskanal for å imøtekomme pasientenes behov for væsker og medisiner. Å ta pasienter med septisk sjokk som eksempel, under redningsprosessen, må en stor mengde krystalloidvæske, kolloidvæske og vasoaktive medisiner suppleres på kort tid. Det sentrale venekateteret kan sikre at disse væskene og medikamentene raskt kommer inn i blodsirkulasjonen og raskt korrigerer sjokktilstanden. Samtidig kan hemodynamisk overvåking også utføres gjennom det sentrale venekateteret. Legen kobler trykksensoren til katetergrensesnittet for å oppnå parametere som sentralt venetrykk og lungearteriekiletrykk i sanntid, noe som hjelper legene til å forstå pasientens hjertefunksjon og blodsirkulasjonsstatus i sanntid, og gir et viktig grunnlag for å formulere nøyaktige behandlingsplaner.
Ved tumorbehandling er mange cellegiftmedisiner svært irriterende for blodkar, og administrering gjennom perifere årer kan forårsake komplikasjoner som flebitis. Det sentrale venekatetersettet kan plassere et kateter i den sentrale vene, slik at cellegiftmedisiner direkte kan komme inn i de store blodkarene og raskt fortynnes, og dermed redusere irritasjonen til blodkarene, redusere sannsynligheten for komplikasjoner og forbedre pasientenes behandlingstoleranse og etterlevelse. For eksempel kan brystkreftpasienter som får svært irriterende cellegiftmedisiner som doxorubicin bruke sentrale venekateter for å effektivt unngå alvorlige konsekvenser som hudnekrose og vevssåring forårsaket av medikamentekstravasasjon. Samtidig, for pasienter som trenger langvarig og multippel cellegift, reduserer sentrale venekatetre smerten ved gjentatte punkteringer og forbedrer kontinuiteten i behandlingen.
I tillegg, i ernæringsstøtteterapi, kan sentrale venekateter brukes til total parenteral ernæringsstøtte for pasienter som ikke kan ta inn nok ernæring gjennom mage-tarmkanalen, for eksempel pasienter med langvarig koma og alvorlige forbrenninger. Å gi høykonsentrasjon, høykalori-næringsoppløsning gjennom den sentrale vene kan dekke pasientens kropps behov for næringsstoffer og fremme pasientens utvinning. Å ta pasienter med omfattende forbrenninger som eksempel, undertrykkes gastrointestinalfunksjonen på grunn av traumer, og de kan ikke fordøye og absorbere mat normalt. På dette tidspunktet gis den alt-i-ett-næringsoppløsningen som inneholder aminosyrer, fettemulsjon, glukose og andre ingredienser gjennom det sentrale venekateteret for å opprettholde pasientens nitrogenbalanse, fylle på energien som kreves av kroppen og akselerere sårheling. Samtidig kan medisinsk personell også overvåke pasientens elektrolytter, blodsukker og andre indikatorer gjennom det sentrale venekateteret og justere ernæringsstøtteplanen i tide.
Strenge og standardiserte driftsprosedyrer
De operating procedures of the central venous catheter kit need to strictly follow the specifications and standards. Before the operation, the doctor needs to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the patient's condition, including the patient's age, weight, underlying diseases, coagulation function, etc., and select the appropriate puncture site and central venous catheter type. Common puncture sites include the internal jugular vein, subclavian vein and femoral vein. Different sites have their own advantages and disadvantages, and they need to be carefully selected according to the specific situation of the patient. At the same time, detailed explanations and communication should be given to the patient, and the patient should be informed of the operation process, possible risks and key points of cooperation to obtain the patient's cooperation. During the operation, the principle of aseptic operation must be strictly followed. The puncture site must be disinfected with iodine more than three times, and the diameter of the disinfection range must not be less than 15 cm. A large sterile sheet must be laid to ensure that the entire operation is carried out in a sterile environment. Then follow the steps of trocar puncture, guide wire insertion, dilation with a dilator, insertion of a removable sheath, insertion of a central venous catheter, fixation of the catheter, and connection of an external interface. Taking internal jugular vein puncture as an example, under ultrasound guidance, after determining the puncture point, the trocar is inserted at an angle of 30-45 degrees. After seeing the blood return, it is confirmed that it is in the vein, and then the subsequent components are inserted according to the process. After the operation is completed, the patient needs to be closely observed and cared for, and the patient must be monitored for complications and treated in a timely manner. This includes observing whether the puncture site is red, swollen, or exuded, and changing the dressing regularly; monitoring the patient's body temperature, blood routine, and other indicators to determine whether an infection has occurred; evaluating the function of the catheter to ensure smooth infusion, blood collection, and other operations.
Utfordringer og risikoer står overfor
Selv om sentrale venekatetersett spiller en viktig rolle i det medisinske feltet, står de også overfor noen utfordringer og risikoer under bruk. Infeksjon er en av de vanligste komplikasjonene av sentrale venekateter. Siden kateteret blir liggende i kroppen i lang tid, er det lett for bakterier og andre mikroorganismer å invadere, noe som forårsaker lokal infeksjon eller systemisk infeksjon. Bakterier kommer hovedsakelig inn i kroppen gjennom hudkolonisering på punkteringsstedet, forurensning av kateterkontakten og forurensning av infusjonssystemet. Trombose er også et problem som ikke kan ignoreres. Kateteret kan stimulere det vaskulære endotelet i blodkaret, og forårsake endringer i blodkoagulering, og dermed danne en trombe. Når tromben faller av, kan det forårsake alvorlige komplikasjoner som lungeemboli. I tillegg kan problemer som kateterblokkering og forskyvning også påvirke normal bruk og behandlingseffekt av det sentrale venekateteret. Kateterblokkering kan være forårsaket av medikamentavsetning, blodkoagulering osv.; Kateterforskyvning kan være relatert til faktorer som feil pasientaktivitet og løs fiksering.
For more information, please call us at +86-18913710126 or email us at .
Vaskulære intervensjonsprosedyrer er integrert i moderne kardiovaskulær medisin, spesielt når det...
Introduksjon Enkeltlumen endobronkial tube s er en kritisk komponent ...
I moderne medisin er medisinske katetre uunnværlige verktøy som brukes i et bredt spekter av beha...
I helsesektoren kan viktigheten av å velge riktige materialer for medisinsk utstyr ikke overvurde...
I en tid med presisjonsmedisin bærer et lite rør ofte vekten av livreddende ansvar. Som et kjerne...
I moderne helsevesen er presis væskehåndtering avgjørende for pasientsikkerhet og behandlingseffe...